The blepharospasm is a condition that causes involuntary contractions of the muscle around the eye. These contractions can be annoying and affect the daily life of sufferers. There are different types of blepharospasm, and symptoms can vary. It is important to know the causes, risk factors and treatment options to manage this condition properly.
What is blepharospasm
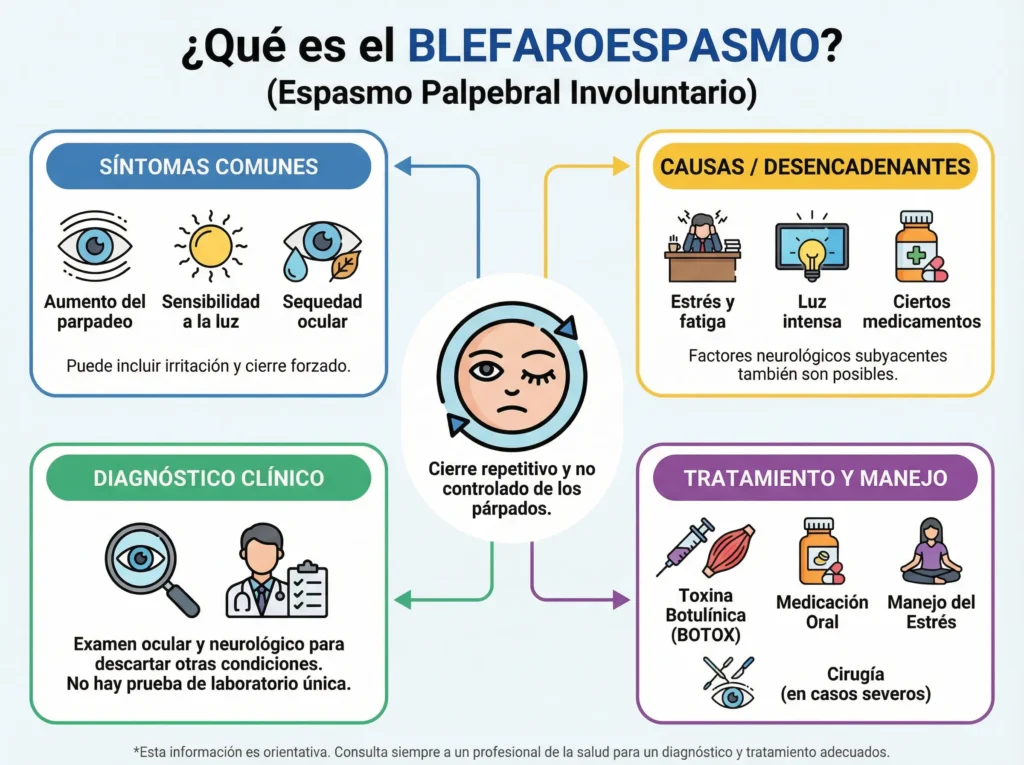
It is a neurological disorder that causes involuntary contractions of the muscles surrounding the eyes, especially the orbicularis oculi muscle. These contractions can be sporadic or recurrent, and can lead to complete closure of the eyelids. Sufferers can experience significant difficulties when trying to perform everyday tasks, which impacts on their quality of life.
Blepharospasm is classified as a focal dystonia, which means that it affects movement in a specific region of the body, in this case, the eye area. The blinking becomes uncontrollable and can vary in intensity, making simple activities such as reading, driving or watching television difficult. This disorder may arise without an apparent cause or as a result of other medical conditions.
Some of the more characteristic symptoms of this disorder include:
- Involuntary contraction of the eyelid.
- Excessive and difficult to control blinking.
- Temporary closure of the eyes that may block vision.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
- In some cases, spasms may occur in other parts of the face.
It is essential to note that the diagnosis and assessment of the severity of blepharospasm should be made by a healthcare professional, as there are several factors that can play a role in the occurrence of this condition. Seeking medical attention is crucial to determine the appropriate treatment and improve daily functionality.
Types of blepharospasm
Blepharospasm can be divided into two main categories, each with distinctive characteristics that affect individuals differently.
Benign essential blepharospasm
This type is the most common. It occurs without a clear underlying cause and usually occurs sporadically. The contractions can range from short episodes to longer periods and, in some cases, can significantly affect day-to-day functionality.
Secondary blepharospasm
This type is associated with other medical conditions. It is usually the result of factors such as:
- Prolonged eye fatigue.
- Emotional or physical stress.
- Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease.
- Disorders such as Tourette's syndrome.
The characteristics of secondary blepharospasm may vary depending on the disease causing it, and treatment may also need to address the underlying condition for best results.
Both types of blepharospasm can affect quality of life, and it is essential to recognise the differences in order to implement appropriate management. Accurate identification of the type can help define the most effective treatment strategies for each case.
Symptoms of blepharospasm
The symptoms of this condition often vary from person to person, but there are certain common manifestations that can be observed. It is important to be aware of these signs, as they can significantly affect everyday life.
- Uncontrollable eyelid twitchingThe most prominent feature is repetitive contractions of the eyelid muscles, which may prevent the eyes from opening. These contractions can be sporadic or prolonged, even making it difficult to see.
- Difficulty in carrying out daily activitiesConstant interruptions in the ability to keep the eyes open can make everyday tasks, such as reading, using the computer or driving, difficult or almost impossible.
- Increased sensitivity to lightMany affected people experience increased sensitivity to light, which can intensify episodes of twitching and increase general discomfort.
- Blurred visionDuring spasms, vision may become temporarily blurred, which can be worrying and frustrating in situations where visual clarity is required.
- Facial contractionsIn some cases, these spasms are not limited to the eyelid. Some people may also experience involuntary twitching in other parts of the face, which can add an extra degree of discomfort.
Identifying these symptoms early can facilitate diagnosis and help to seek appropriate treatment. Understanding how these signs present is essential to effectively manage the condition.
Causes and risk factors
The aetiology of blepharospasm can be complex and, in many cases, no clear origin is identified. However, there are a number of factors that can trigger or aggravate this condition. Understanding these is important for effective symptom management.
Among the most common causes are:
- FatigueExtreme tiredness can cause episodes of involuntary muscle contractions of the eyelid.
- StressEmotional stress often has an impact on the nervous system, which can trigger spasms.
- Caffeine and alcohol consumptionThese substances may sensitise the neuromuscular system and contribute to episodes of blepharospasm.
- MedicinesSome drugs, especially those for the treatment of migraines, can have side effects including twitching of the eyelids.
- Underlying health problemsBlepharospasm can be a symptom of more serious conditions, such as Parkinson's disease or Meige's syndrome.
Identification of risk factors may also be relevant. People most likely to develop this condition include those who:
- They are between 40 and 60 years old.
- Have a family history of dystonia or related disorders.
- They are women, as they have been found to be more predisposed to this disorder.
Awareness of these factors allows you to be more alert and to take preventive measures. However, it is essential to see a specialist for proper assessment if you experience related symptoms.
Diagnosis of blepharospasm
Evaluation of blepharospasm requires a comprehensive approach by a specialist. Generally, the first step is to take a complete medical history, including a review of both the patient's medical and family history. It is essential to gather information about current symptoms and their evolution over time.
Eye examinations are used to rule out other pathologies that may be mimicking the symptoms. These tests assess visual function and determine whether there are other eye health problems.
Occasionally, a neurological evaluation may be necessary. This helps to identify if there are underlying neurological disorders contributing to the manifestation of blepharospasm. Referral to a neurologist can be key to establishing an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnostic methods may include:
- Comprehensive eye examinations
- Screening for family history of dystonia or neurological disorders
- Observation of blinking and twitching patterns
- Assessment of light sensitivity and other associated symptoms
It is important that the diagnosis is made carefully, as misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment. For this reason, specialists often take time to analyse each case individually.
Once the diagnosis has been established, different treatment options can be considered, which will be tailored to the specific needs of each patient. Clear communication between the specialist and the patient is vital in deciding the most appropriate approach to the management of this condition.
If you notice repeated eyelid twitching or difficulty keeping your eyes open, don't wait for it to get worse. Dr Ali Nowrouzi, ophthalmologist in Marbella specialising in complex ocular pathology, can assess your case and propose the most appropriate treatment.
👉 Ask for your personalised assessment and regain a more comfortable vision in everyday life.
Treatments available
There are various options to address blepharospasm, and the appropriate treatment will depend on the severity of symptoms and individual patient characteristics. Personalisation in the therapeutic approach is key to achieving the best outcome.
One of the most common treatments is the botulinum toxin injections, popularly known as Botox. This procedure involves injecting the toxin directly into the muscles surrounding the eyelid. Botox blocks nerve impulses, which helps to reduce the activity of the muscles responsible for the contractions. Typically, these injections are required every three to four months.
Other treatment alternatives
If Botox injections do not offer the best response, other options may be considered, such as:
- Oral medicinesSome drugs can help reduce muscle spasms, although these may have significant side effects.
- Surgical interventionIn severe cases where the above alternatives do not offer an effective solution, surgery called myectomy may be chosen. This procedure involves partial removal of the muscles that control blinking. In selected cases, it may be necessary to consider a eyelid surgery to improve palpebral function and patient comfort.
- Lifestyle changesImplementing strategies to reduce stress and regulate caffeine and alcohol consumption may be beneficial in mitigating episodes.
- Treatment of related conditionsIf blepharospasm is secondary to some other condition, addressing that underlying condition may alleviate symptoms.
Each treatment has its advantages and disadvantages, so it is essential to discuss with a specialist which may be the most appropriate. Management of this condition may require a multidisciplinary approach and regular monitoring to ensure steady improvement.
Long-term prognosis and management
The prognosis for those suffering from blepharospasm varies considerably between individuals. Many manage to improve their symptoms with appropriate treatments and lead a more satisfactory daily life. The effectiveness of therapies will depend on a number of factors, including the severity of the condition, response to treatments and the presence of associated medical conditions.
It is important to follow up regularly with the specialist. This allows treatments to be adjusted and any changes in symptoms to be addressed. Appropriate management may involve:
- Periodic botulinum toxin injections, which are usually the most effective option.
- Oral medications if injections do not provide the desired relief.
- A personalised plan that considers factors such as daily activity and lifestyle.
The duration of the effects of treatments can vary. Many patients report that botulinum toxin injections are effective for a few months, but eventually the procedure needs to be repeated. Regularity of treatment is key to prevent spasms from intensifying over time.
Sometimes the condition can be associated with other neurological disorders, complicating the prognosis. For this reason, it is essential to have a check-up with a neurologist if other symptoms or warning signs are present. These professionals can offer a broader view and help improve quality of life without compromising eye health.
Blepharospasm doesn't have to limit your life. With an individualised plan that combines effective treatments and regular follow-up, many patients return to driving, reading and working normally.
👁️ If you live on the Costa del Sol, you can make an appointment Dr. Ali Nowrouzi in Marbella to study your case and design a tailor-made treatment for you.
Advances and new developments in the treatment of blepharospasm
In recent years, research into blepharospasm has led to several advances in its treatment, giving hope to patients. The medical community continues to explore new ways to address the condition, seeking to improve the quality of life for sufferers.
One of the most significant innovations has been the use of botulinum toxin injections. These injections have been refined over time, allowing for more precise dosing and longer duration of effect. In addition, new formulations are being studied to minimise side effects and extend their efficacy to a wider population.
In the field of oral medicines, research is underway into drugs that may be more effective and have fewer adverse effects than current treatments. These new options offer the possibility of more appropriate and personalised therapeutic responses for each patient.
In terms of surgical techniques, myectomy has evolved. Studies are underway on less invasive surgical alternatives, which could benefit those seeking options more suited to their needs. Research in this area focuses on achieving optimal results with reduced recovery time.
- Development of new botulinum toxin injection techniques.
- Study of new oral drugs with fewer side effects.
- Research into less invasive surgical procedures.
Finally, telemedicine is increasingly being used for the monitoring and management of this condition. This not only facilitates access to specialised care, but also allows for more continuous monitoring of symptoms and adjustments in treatment in real time.
Research efforts are focused on increasing the understanding of blepharospasm, which in turn may lead to the identification of more effective and targeted treatments. These developments are cause for optimism and open the door to better prospects for those affected.
If these symptoms affect your day-to-day life, it is essential that you consult a doctor. ophthalmologist in Marbella to assess a personalised and safe treatment.